Language
Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 11-25-2025 Origin: Site
Many users who are new to laser cutting frequently confuse CO2 and fiber lasers, not knowing which one best suits their machining requirements. These two types of lasers are actually intended for quite distinct uses.
Metal fabrication is the focus of fiber laser cutting machines.
High cutting speed, superior edge quality, the capacity to cut intricate geometries, and smooth cut surfaces with the appropriate power—often without the need for post-processing—are all provided by them.
CO2 lasers are mostly utilized for non-metal materials like acrylic, wood, plastic, leather, fabric, MDF, and paper, especially low-power ones under 500W cannot cut metal materials. If you would like to cut metal, normally the power more than 500W is needed.
We will discuss the specific distinctions between CO2 and fiber lasers in another article because they have somewhat diverse uses. In this guide, we focus specifically on what materials a fiber laser cutting machine can cut.
Fiber lasers excel at cutting a wide range of metallic materials. Below is a breakdown of the most common metals and alloys.
Carbon steel is one of the easiest materials for fiber lasers to cut due to its excellent absorption of the laser wavelength.
Typical applications: construction, machinery parts, containers, automotive components.
Benefits when cutting carbon steel:
High cutting efficiency
Clean edges
Supports high-speed production
Key notes: Oxygen-assisted laser cutting creates a clean, shiny cut on carbon steel.
Stainless steel reflects less laser energy than aluminum or copper, making it highly compatible with fiber laser
systems.
Common industries: kitchenware, medical devices, food equipment, electronics.
Advantages:
Smooth and bright cutting edges
Minimal burring with nitrogen cutting
Excellent for thin-to-medium thickness plates
Key notes: Nitrogen cutting recommended for better edge quality.
Aluminum has high reflectivity and heat conductivity, making it more challenging to cut than steel.
However, with today’s high-power fiber lasers (6kW+), aluminum is widely processed for:
Aerospace components
Automotive frames
Electrical enclosures
Outdoor products
Key notes: Requires higher power than steel at the same thickness.
Because of their great reflectivity, these materials need reliable high-power sources and laser systems with increased
safety. Brass and copper are frequently utilized in:
Electrical components
Ornamental elements
Heat exchangers
Hardware products
Key notes: To reduce the possibility that the materials won't be cut through, it is preferable to select a higher power.
Titanium and superalloys (based on nickel) are commonly utilized in:
Aerospace and Aviation
Medical Implants
High-heat-resistant components
Fiber lasers offer:
Narrow kerf width
Minimal heat-affected zone.
High precision for premium applications.
These materials are often more difficult to work with traditional mechanical cutting, making laser cutting the preferred option.
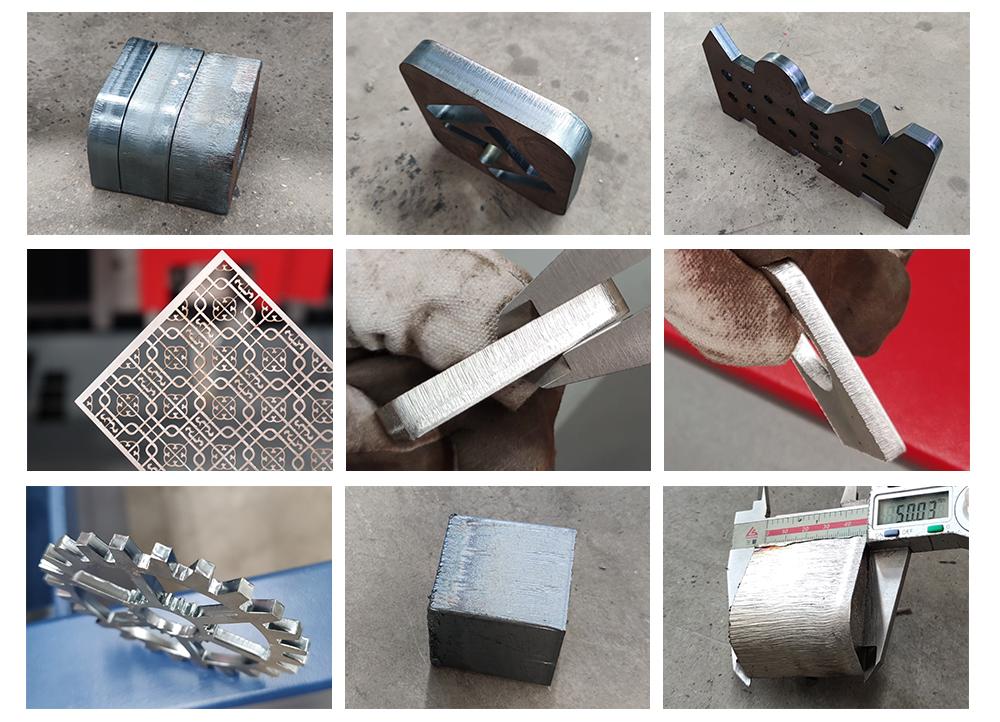

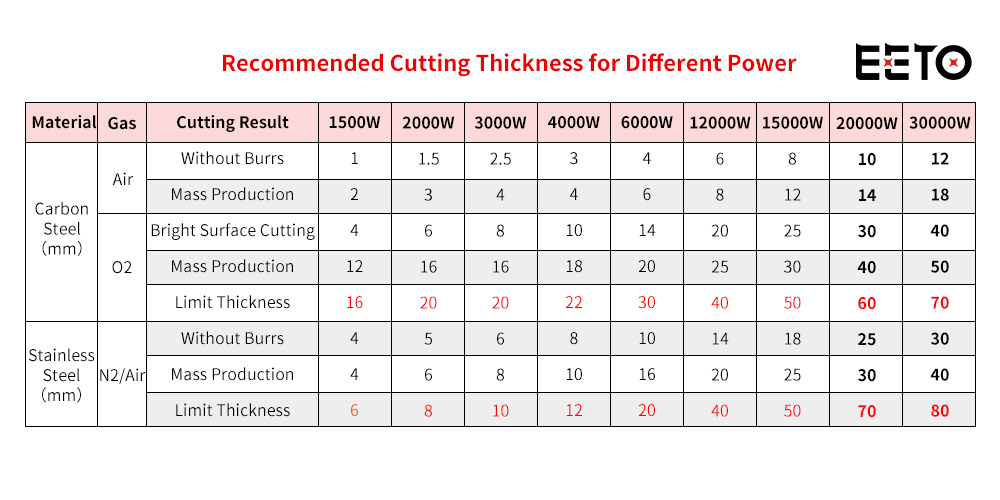
Different metals absorb laser energy differently, so the same laser power cuts each material with different maximum thicknesses.
For example:
If a user frequently cuts 16 mm carbon steel and 10 mm aluminum:
A 3kW laser can handle 16 mm carbon steel
But 3kW is NOT enough to cut 10 mm aluminum
Aluminum requires at least 6kW
Therefore:
✔ Always choose your laser power based on the most difficult material in your machining range.
✔ Higher power = higher speed for the same thickness → higher productivity.
If you are unsure how to select the right laser source, our team can help you evaluate your materials, thicknesses, and production needs.
Yes, the sort of machine you require depends on the shape of your metal (sheet, tube, or structural steel). We designed the metal fiber laser cutter listed below based on the processing requirements of users:
Only for flat metal sheets
Cannot cut tubes
Suitable for general fabrication, chassis, stainless products, mechanical parts
The single table model is suitable for those who do not have a high processing requirement, but the exchange table may operate continuously for 24 hours, making it suitable for those who have a lot of work to perform. We also have a Gantry-type Laser Metal Cutting Machine suitable for industries that require the cutting of heavy and big metal format sheets (Now this model is widely used in the shipbuilding industry, you can know more from this blog: Why Shipbuilders Prefer Gantry Type Fiber Laser Cutter For Large Thick Steel Plates?) As well as an FCS Model suitable for those who value safety and the environment but have limited working space, please see the link below for additional information on each.
→ (Check Metal Sheet Laser Cutting Machines Product List)

For round, square, rectangular, oval tubes, and H beams, I beams, angle steel and etc.
Cannot cut sheet metal.
Ideal for furniture, exercise equipment, cars, and metal frames.
We have a variety of chuck sizes to meet the processing demands of both small and large pipes, and we can also provide semi-auto loading or auto-loading systems based on the needs of our clients to optimize cutting speed.
→ (Check Pipe Cutting Machines Product List)
Cuts both sheet metal and tubes
Ideal for users with various processing needs but limited budget
Suitable for those with a high volume of metal sheet cutting and minimal pipe cutting requirements.
→ (Link to Pipe & Sheet Combo Machine Product List)
Designed for heavy-duty materials such as H-beams and large profiles
Commonly used in steel structures and construction industry
→ (Link to EETO-FHS Beams & Profiles Fiber Laser Cutting Machine Page)
Now that you understand the materials and thicknesses a fiber laser cutting machine can handle — and how different machine types serve sheet, tube, and structural applications — you can make a more informed decision for your production needs.
If you need help evaluating your materials, thickness range, or laser power selection, our engineering team is ready to assist you. Contact us anytime for professional guidance and customized solutions.
